HTH™ makes
Pool and Spa care easy.
Our balancers, sanitizers, shocks, and algaecides are designed with DIY pool owners like you in mind.

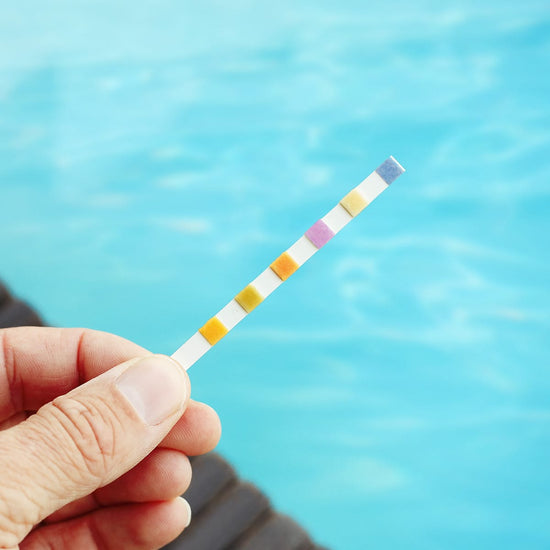
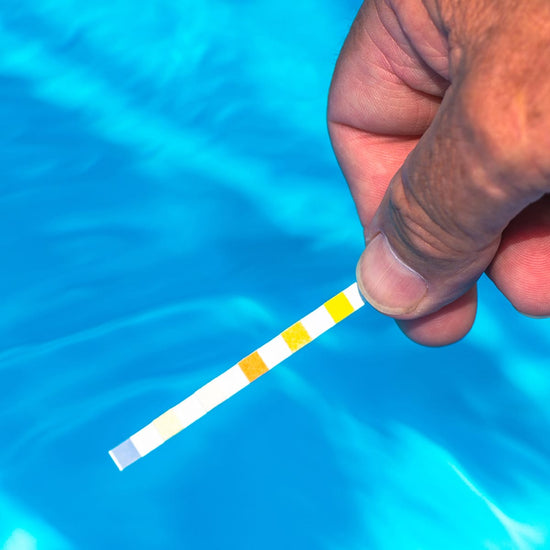
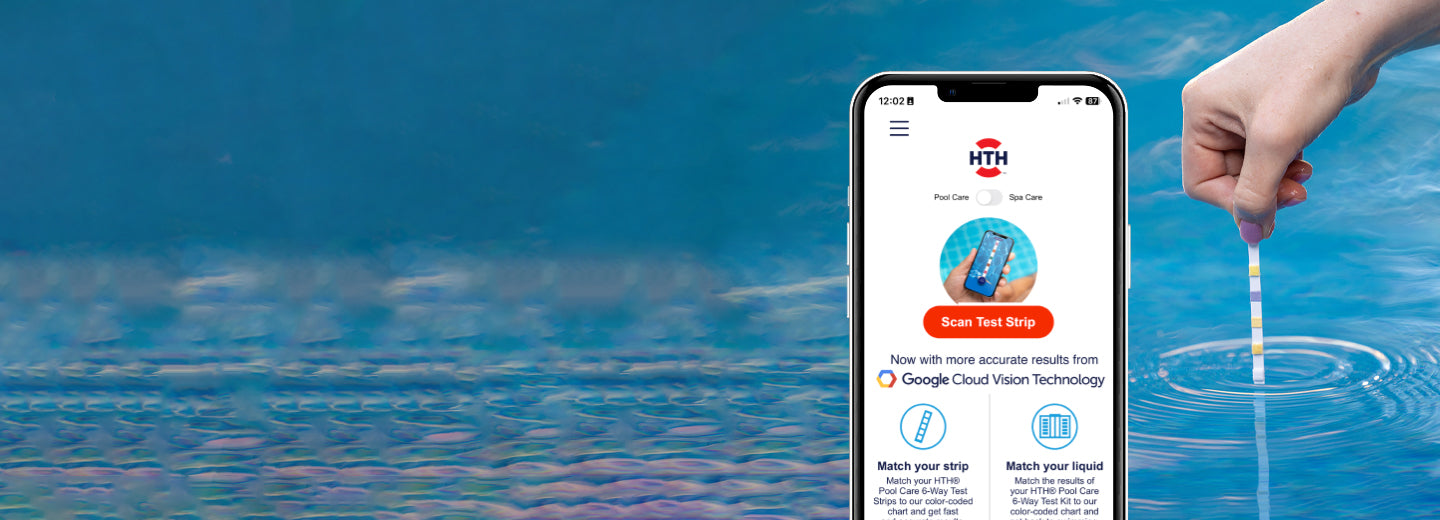
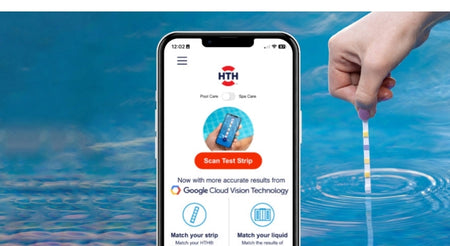
Have you tested your pool water lately?
Twice weekly water testing is fast and easy with HTH™ Test to Swim™ app, now with more accurate results from Google Cloud Vision Technology.